Industrial
Industrial Application - Electronic Thermostat
Thermostats are used to monitor and regulate the temperature of an indoor area. An electronic thermostat senses temperature, such as with a thermistor or thermocouple, and returns an electrical signal to the rest of the heating, ventilation, and air conditioning ( HVAC ) system, indicating which functions (e.g. heating, cooling, etc.) should be enabled.
Without some form of thermostat, an HVAC system would have no feedback or control, making it costly, wasteful, and unable to maintain a consistent temperature. Electronic thermostats that keep track of the local time and the day of the week can be programmed with temperature profiles that help minimize energy expenses and maximize comfort.
Although many of the functions of a simple electronic thermostat can be handled in a single application specific integrated circuit (ASIC), there may be any number of reasons for implementing a design using multiple individual components. The flexibility of employing discretes allows for added safety, accuracy, part redundancy, or additional functionality, such as touchscreen support.
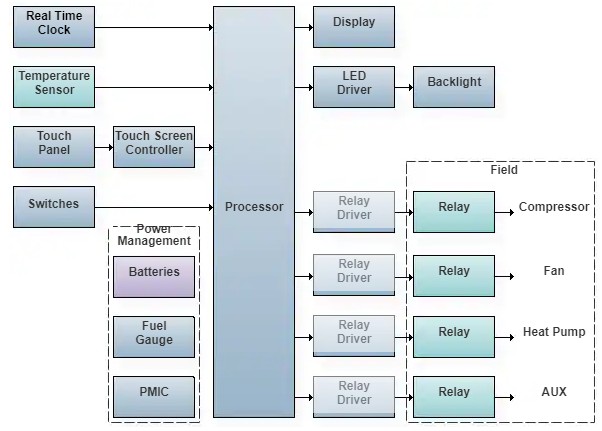
Major subsystems include:
- User I/O: display and keypad or touchscreen, speaker, etc.
- Temperature sensing circuitry
- Microcontroller or processor
- Power management
Electronic Thermostat Block Diagram
This design is for reference only. The design, as well as the products suggested, has not been tested for compatibility or interoperability.